 Range Sum of BST
Range Sum of BST
November 18, 2020
I’m trying to get in a habit of starting my mornings off with coffee and a Leetcode problem before work. Ease my way into the day and get the brain juices flowing. Let’s jump in!
Given the root node of a binary search tree, return the sum of values of all nodes with a value in the range [low, high].
Example 1:
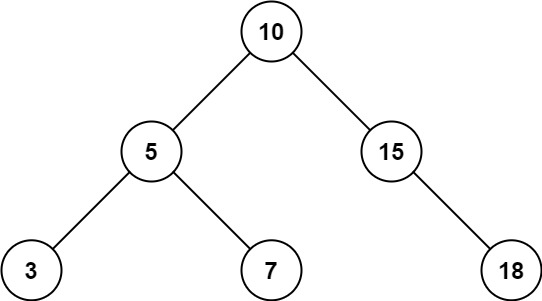
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
Output: 32
Example 2:
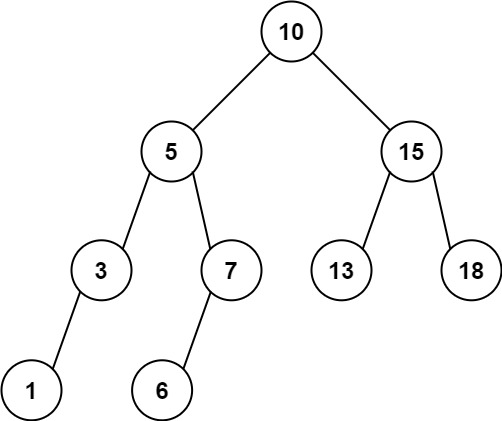
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
Output: 23
Constraints:
* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 2 * 104].
* 1 <= Node.val <= 105
* 1 <= low <= high <= 105
* All Node.val are unique.
This appears to be a simple traversal where DFS or BFS will suffice. A full traversal will get the required sum value but we can optimize it where we can ignore certain left/right child nodes based on the current node value. Simply put, if the current node value is less than the range lower bound, we can ignore all left children of this node, since all of those node values will be less than the current. This rule can be applied to the right side as well, just ignoring values above the upper bound.
I don’t think I missed any this time.
None that I can think of. Just the standard recursive vs. iterative trade offs.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
import collections
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
queue = collections.deque([root])
result = 0
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
is_low = low > node.val
is_high = high < node.val
# If the value is in range, include it in our sum.
if not is_low and not is_high:
result += node.val
left, right = node.left, node.right
# Don't traverse left if the current value is less than
# our lower bound since all values "further" left will be less than
# the current.
if not is_low and left:
queue.append(left)
# Don't traverse right if the current value is more than
# our upper bound since all values further right will be more than
# the current.
if not is_high and right:
queue.append(right)
return result
Runtime: 200 ms, faster than 90.29% of Python3 online submissions for Range Sum of BST.
Memory Usage: 22 MB, less than 91.37% of Python3 online submissions for Range Sum of BST.